AI vs Manual Coding: Speed and Quality Comparison
AI-assisted coding outpaces manual methods for routine tasks, saving time and increasing productivity. However, manual coding excels in quality, especially for complex, secure, and critical systems. Here's a quick breakdown:
-
AI Coding Strengths:
- Speeds up repetitive tasks like boilerplate creation, documentation, and refactoring (up to 90-95% faster).
- Reduces onboarding time and boosts throughput (e.g., AI users average 2.3 pull requests weekly vs. 1.4 manually).
- Enhances efficiency for small teams and startups, with tools automating up to 95% of codebases.
-
Manual Coding Strengths:
- Produces more secure, maintainable, and accurate code.
- Handles intricate logic, architectural designs, and critical systems better.
- Avoids AI pitfalls like increased code warnings, complexity, and vulnerabilities.
Quick Comparison
| Aspect | AI Coding | Manual Coding |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster for repetitive tasks (up to 90%) | Slower but consistent across tasks |
| Security | Higher risk of vulnerabilities | Better for secure and critical systems |
| Accuracy | More prone to errors | Fewer defects, better for complex logic |
| Maintainability | Prone to technical debt | Designed for long-term upkeep |
Blending both methods often yields the best results: AI accelerates routine tasks, while manual coding ensures quality and reliability.
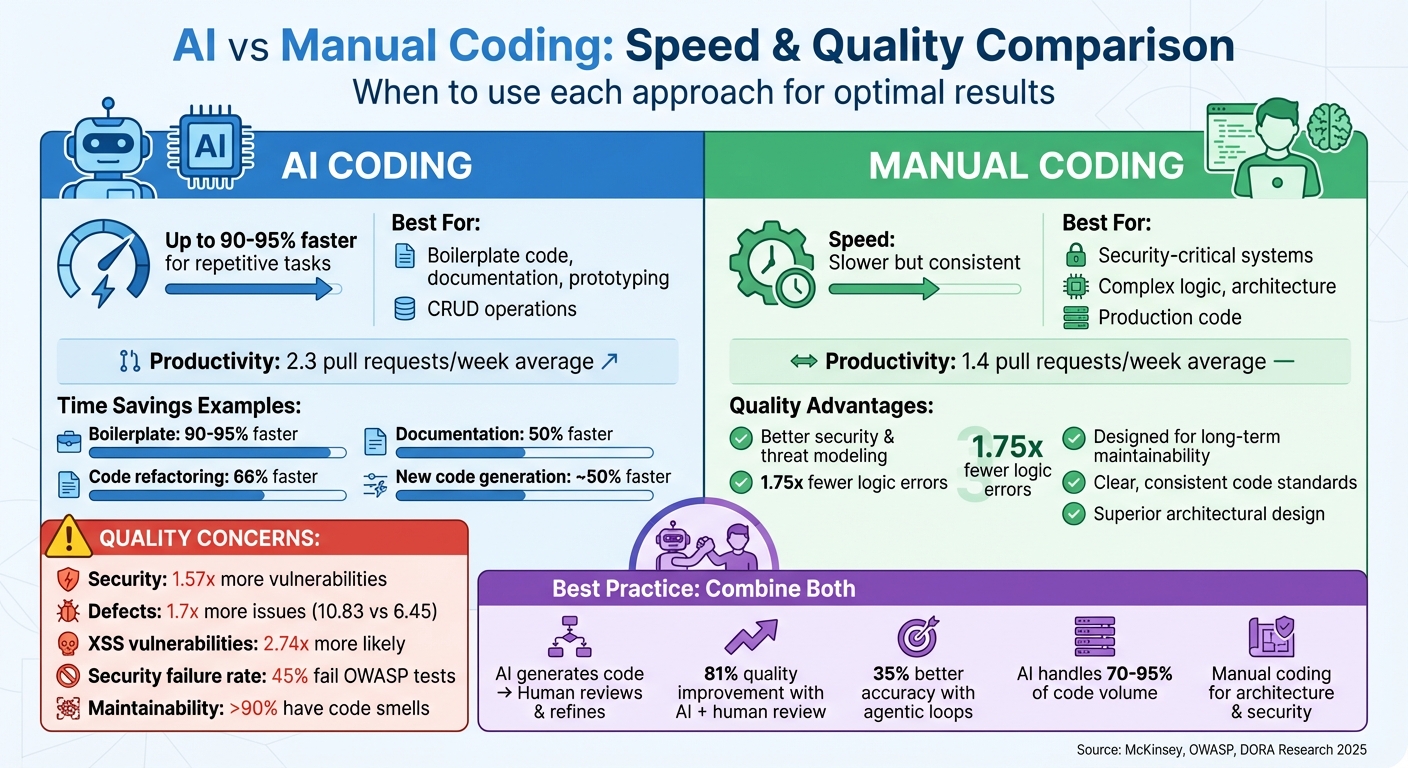
AI vs Manual Coding: Speed, Quality, and Security Comparison
Speed Comparison: AI vs Manual Coding
How AI Speeds Up Coding
AI tools dramatically reduce the time it takes to complete coding tasks by automating repetitive and time-consuming processes. According to McKinsey, developers using generative AI can finish coding tasks up to twice as fast compared to traditional methods [4]. For example, documentation takes 50% less time, creating new code is about 50% faster, and refactoring code is completed in roughly 66% of the time it would take manually [4].
The most striking improvements are seen in what's often called "vibe coding" - where you describe what you need in plain English and let the AI generate the code. Take these examples: In March 2025, Aakash Gupta and Colin Matthews prototyped five distinct product features in just 84 minutes using tools like Bolt, Cursor, and Lovable [5]. Similarly, in June 2025, Md. Sohel Rahman built a full SaaS analytics dashboard, complete with authentication, Stripe integration, and real-time charts, in only 40 hours using Lovable. Manually, this project would have taken over 80 hours [6].
Using multiple AI tools together - for example, combining Claude for planning with Cursor for coding - can amplify time savings by 1.5 to 2.5 times compared to relying on a single tool [4]. This approach is especially effective for boilerplate code, standard CRUD operations, and getting a project off the ground. In some startups, AI now generates over 95% of the codebase, showcasing how transformative these tools have become [7]. The time saved with AI stands in stark contrast to the slower, more methodical pace of manual coding.
Why Manual Coding Takes Longer
Manual coding is slower because it requires developers to handle everything themselves - writing code from scratch, setting up environments, and figuring out how to approach a blank screen. For repetitive tasks, the time difference is glaring, as shown in the table below.
However, the gap shrinks when it comes to complex coding tasks. For projects involving unfamiliar frameworks or requiring a deeper level of "big-picture" thinking, AI's speed advantage drops to less than 10% [4]. This highlights AI's strength in routine, repetitive jobs while emphasizing the continued importance of manual coding for more intricate work. A participant in the McKinsey study explained:
"Generative AI is least helpful when the problem becomes more complicated and the big picture needs to be taken under consideration" [4].
Interestingly, junior developers may find AI less helpful in some cases. Without a strong grasp of foundational coding principles, they might spend 7–10% more time resolving errors introduced by AI-generated code [4].
Speed Comparison Table
| Task Type | AI Time | Manual Time | Time Savings % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boilerplate | 2–5 minutes | 1–2 hours | 90–95% |
| Documentation | 30 minutes | 1 hour | 50% |
| New Code Generation | 1 hour | 2 hours | ~50% |
| Code Refactoring | 20 minutes | 1 hour | 66% |
| Complex Logic | 2.2 hours | 2 hours | –10% (slower) |
sbb-itb-c336128
Quality Comparison: AI vs Manual Coding
Quality Issues with AI-Generated Code
AI-generated pull requests tend to have more defects - 1.7 times more, to be exact - averaging 10.83 issues compared to 6.45 in manually written code [12]. This isn't just about quantity; the nature of the defects is concerning. AI code is 2.74 times more likely to introduce Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities, 1.91 times more likely to create insecure object references, and 1.88 times more likely to mishandle passwords [12].
In a 2025 evaluation of over 100 AI models, only about 55% of the generated code passed basic security checks [15]. Java emerged as the riskiest language, with a staggering 72% security failure rate, followed by C# (45%), JavaScript (43%), and Python (38%) [14]. Adding to the challenge, over 90% of the issues in AI-generated code are attributed to "code smells" - flaws that make the code harder to maintain [10]. Tariq Shaukat, CEO of Sonar, sums it up well:
"You're almost being lulled into a false sense of security" [10].
These findings highlight why manual coding remains indispensable for systems where security and reliability are critical.
Quality Benefits of Manual Coding
Manual coding offers a level of precision and reliability that AI struggles to match. It allows developers to design complex system architectures thoughtfully, ensuring better control of data and logic flow across multiple functions - something AI models often struggle with due to their limited understanding of deeper semantics [13][15].
Interestingly, following the widespread adoption of AI in 2025, change failure rates increased by about 30%, underscoring the challenges of relying heavily on AI-generated code [12]. Colin Domoney, a Software Security Consultant, provides a crucial piece of advice:
"Treat AI suggestions as unreviewed code. Never assume AI-generated code is secure. Treat it with the same scrutiny as a snippet from an unknown developer" [8].
For tasks that demand utmost reliability, like secure password handling or complex deserialization, manual coding has a failure rate nearly half that of AI-generated code [12].
Quality Comparison Table
The table below highlights how AI-generated code stacks up against manual coding across key quality metrics:
| Quality Aspect | AI-Generated Code | Manual Coding |
|---|---|---|
| Security | 1.57x more vulnerabilities; 45% fail OWASP Top 10 tests [12][14] | Proactive threat modeling ensures better security [8][11] |
| Logic & Correctness | 1.75x more errors; struggles with complex logic [12] | Excels in handling intricate systems [12] |
| Maintainability | Prone to code smells (>90% of issues) and technical debt [10] | Designed for long-term upkeep and extensibility [8][11] |
| Readability | Verbose, context-unaware, and inconsistent with project conventions [9][10] | Clear, concise, and aligned with team standards [8][9] |
| Structural Complexity | Simple and repetitive [13] | Supports sophisticated architectural designs [13] |
This comparison highlights the trade-offs between the speed of AI-generated code and the reliability, security, and maintainability of manually written code. While AI can be a powerful tool for certain tasks, manual coding remains the gold standard for delivering robust and secure software.
When to Use AI vs Manual Coding
Best Use Cases for AI Coding
AI shines when speed and efficiency are top priorities. For instance, tools like v0 and Bolt can transform screenshots into functional user interfaces in no time, making them perfect for creating demos or MVPs. Teams embracing "vibe coding" - where natural language prompts power app development - can leverage platforms like Emergent and Lovable to build full-stack applications, even without technical expertise.
When it comes to repetitive tasks, AI is a game changer. It can automate up to 40% of boilerplate coding and generate initial scaffolding for features [17]. If you're developing internal tools or simple apps that need to go live quickly, platforms like Replit simplify the process by including built-in databases and authentication, eliminating the need for complex setups. For debugging and refactoring, agentic IDEs like Cursor are invaluable. These tools can analyze entire codebases and suggest multi-file changes. Developers using Cursor have reported that it generates over 70% of the code for specific tasks [16]. In fact, teams adopting Cursor have seen a 3–5x boost in the number of lines of code added during the first month [2].
AI assistants also save significant time. They reduce task durations by 30.7% on average, and for frequent users, that number jumps to 55.9% [3]. It's no surprise that 92% of U.S.-based developers are already integrating AI tools into their workflows [8]. However, when accuracy and security are more critical than speed, manual coding takes the lead.
Best Use Cases for Manual Coding
For projects where security and performance are non-negotiable, manual coding remains essential. This is especially true in industries like finance, healthcare, and high-frequency trading, where precise control and human oversight are necessary for ensuring strong security and peak efficiency. When dealing with complex business logic or niche algorithms, manual coding is better equipped to address intricate edge cases [4][18].
As one expert puts it:
"Treat AI suggestions as unreviewed code. Never assume AI-generated code is secure. Treat it with the same scrutiny as a snippet from an unknown developer" [8].
In these scenarios, the meticulous attention to detail provided by manual coding is indispensable.
AI Systems vs Traditional Coding
Combining AI and Manual Coding
Blending AI with manual coding is proving to be a game-changer for software development, merging speed with solid development practices. Think of AI as a diligent junior developer - it can handle repetitive tasks and generate ideas quickly, but it still needs senior oversight for critical aspects like architecture, security, and managing complex states [6].
A typical workflow might begin with rapid prototyping in cloud tools like Lovable or Bolt. Once the initial framework is set, the code transitions to AI-powered IDEs such as Cursor or Windsurf for fine-tuning and production-level refinement. This combination of quick prototyping and detailed manual oversight creates a streamlined process. For instance, during a one-month trial, AI tools generated nearly all of the code - 197,000 lines across 355 commits - while strict prompts and component limits ensured quality remained intact [21].
Automated feedback systems, known as agentic loops, further enhance this process. These loops allow AI to run compilers, tests, and linters, correcting errors before a human even reviews the code. Armin Ronacher, the creator of Flask, highlighted the value of this approach:
"The agentic flow... went from being not useful at all, to indispensable. The faults of the models are almost entirely avoided because they can run the code and see what happens" [20].
This method has led to a 35% improvement in task accuracy while cutting user effort in half compared to standard AI copilots [19].
To maintain high standards, strict quality control measures are essential. Every piece of AI-generated code should pass through CI/CD pipelines equipped with static linters, formatters, security checks, and at least 80% test coverage [21]. Tools like ClackyAI monitor AI-human collaboration, helping identify areas where manual input is most critical.
With these safeguards in place, the role of developers shifts from writing code to reviewing it rigorously. At Anthropic, for example, 90% of the code for "Claude Code" is produced by AI [20]. However, as Michal Villnow points out, human review remains the bottleneck [21]. This balance - where AI handles the heavy lifting and developers ensure quality - illustrates the path forward for efficient and effective software development.
Conclusion: Speed vs Quality Trade-offs
AI and manual coding complement each other beautifully, with each shining under specific circumstances. Tools like Cursor and Bolt are excellent for tasks like generating boilerplate code, writing unit tests, and creating quick prototypes. However, with this speed comes a trade-off - complexity and code quality can sometimes take a hit. This balance highlights the need for a thoughtful integration of both methods.
Manual coding remains indispensable in situations where reliability is non-negotiable. Whether it's making key architectural decisions, developing security-critical modules, or tackling systems that demand in-depth understanding, human expertise is irreplaceable. These distinctions emphasize the power of blending the two approaches.
By combining AI's efficiency with human judgment, teams can get the best of both worlds. AI can handle repetitive tasks, documentation, and early-stage prototypes, while manual coding steps in for architecture, security reviews, and final quality assurance. Google’s DORA research captures this dynamic perfectly:
"AI's primary role in software development is that of an amplifier. It magnifies the strengths of high-performing organizations and the dysfunctions of struggling ones" [1].
The real challenge lies in scaling your quality assurance to keep up with AI's rapid output. Teams that pair AI-driven code review with human oversight report an 81% improvement in quality, compared to just 55% for those relying solely on AI for generation [22]. Think of AI-generated code as the work of a junior developer - it needs the same level of scrutiny and care to ensure it meets the highest standards.
FAQs
How do AI coding tools boost efficiency for small development teams?
AI coding tools have become a game-changer for small development teams, streamlining workflows by automating repetitive tasks like generating boilerplate code, building test scaffolding, and drafting basic endpoints. By handling these routine jobs, these tools free up developers to concentrate on more complex and impactful work, such as fine-tuning system architecture or enhancing the user experience. Research even suggests that these tools can slash development time for routine tasks by up to 50%, all while maintaining - or even boosting - code quality.
Take tools like Replit Ghostwriter or Vercel's V0 as examples. They can quickly draft API contracts, generate unit tests, and simplify debugging processes. This not only reduces the mental strain on developers but also shortens delivery timelines, allowing small teams to roll out functional products faster - all without the need for a large engineering crew.
What are the risks of using only AI-generated code in development?
Relying solely on AI-generated code can pose serious security risks. Research indicates that close to 45% of AI-created code snippets may have flaws, which can introduce hidden bugs, make maintenance more difficult, and slow down the debugging process. These issues often demand extra layers of review and testing to address.
Additionally, leaning too heavily on AI tools can stunt a developer's skill growth and reduce their control over the codebase. While AI might speed up initial development, it can ultimately slow overall progress, especially when dealing with critical or intricate projects. For these scenarios, manual oversight is crucial to maintain quality, dependability, and long-term viability.
When is manual coding a better choice than using AI tools?
When quality, reliability, or control are top priorities, manual coding often stands out as the better option. While AI tools can accelerate development, they sometimes create inefficiencies. Developers may end up spending additional time reviewing and tweaking AI-generated code, which can actually slow down progress for certain projects. In fact, some studies suggest that relying on AI assistance can hinder workflows, making manual coding a more effective choice for complex tasks.
Manual coding also shines in projects that demand maintainability, compliance, security, or precision - think safety-critical systems or software in tightly regulated industries. AI-generated code often results in bulkier, more intricate outputs, which can complicate testing, debugging, and upkeep over time. For projects that require specialized expertise or fine-tuned performance, manual coding allows developers to maintain greater control, minimizing the chances of hidden bugs or long-term complications.
In the end, developers need to balance speed against control. For high-stakes projects or when long-term reliability is essential, manual coding remains a trusted approach.









