Code Review Checklist for AI-Generated Code
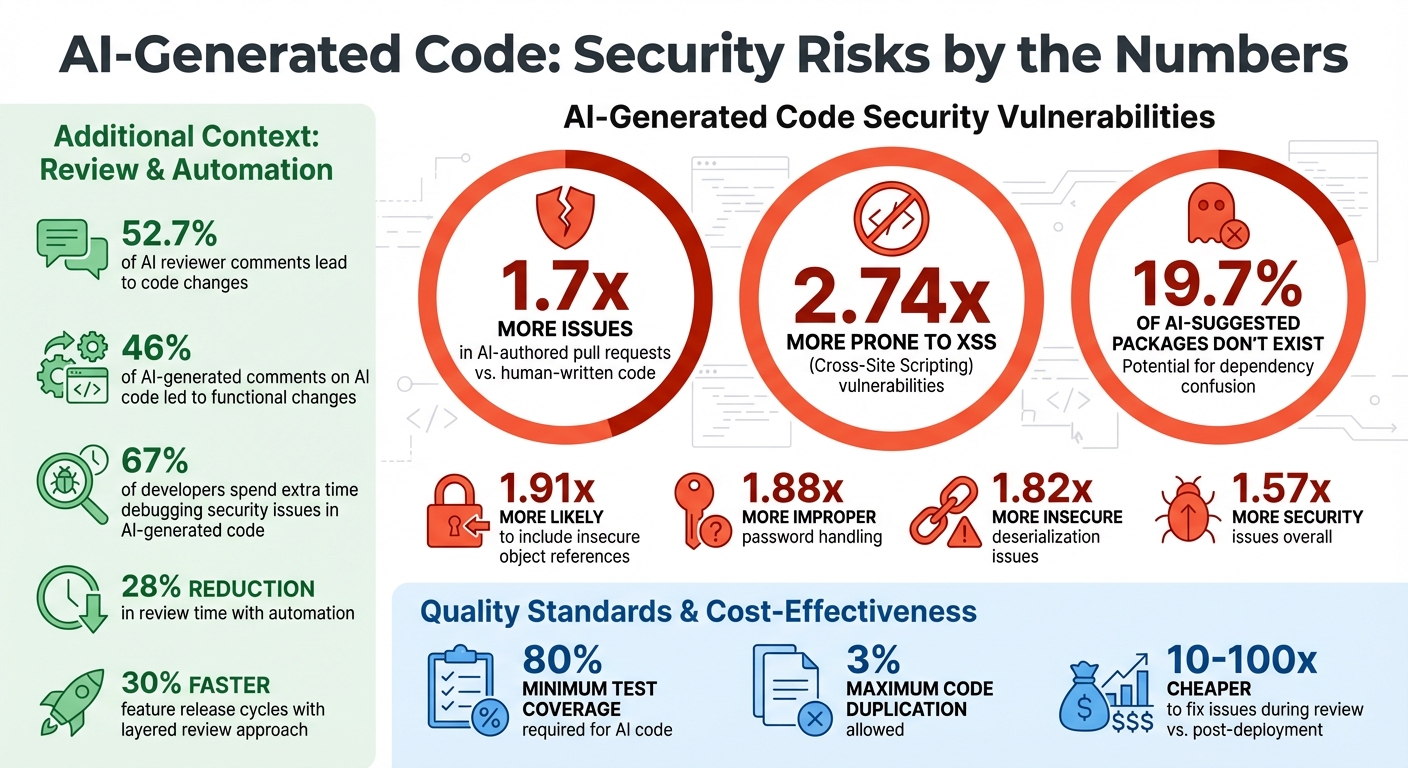
AI-generated code can save time, but it often introduces more errors and security risks than human-written code. Studies show AI-authored pull requests contain 1.7x more issues and are 2.74x more prone to XSS vulnerabilities. To ensure quality, every line of AI-generated code needs thorough review.
Here's how to approach it:
- Functional Correctness: Validate the code against requirements, check edge cases, and run automated tests.
- Security: Audit for vulnerabilities like unsanitized inputs, hardcoded secrets, and dependency risks.
- Code Quality: Ensure readability, adherence to style guides, and avoid redundant or verbose code.
- AI-Specific Risks: Watch for hallucinated APIs, license violations, and "slopsquatting" (fake packages).
Key tools like SonarQube, Semgrep, and Dependabot can automate checks, but human oversight remains critical. Following a structured checklist minimizes errors, improves security, and ensures production readiness.
AI-Generated Code Security Risks and Vulnerabilities Statistics
Review your AI's Code - A Simple Process for Building More Robust Systems Faster with AI
sbb-itb-c336128
Functional Correctness Checklist
When working with AI-generated code, one of the most common pitfalls is functional correctness. While the code might compile and look well-structured, it often misses critical business requirements or relies on flawed assumptions about your system. That’s why it’s crucial to treat AI-generated code as a starting point rather than production-ready work [2][3].
Match Code to Requirements
Begin by cross-checking the AI-generated code against your project documentation, design specifications, and established code patterns. AI tools don’t have the full picture - they’re unaware of your architectural decisions, business constraints, or long-term goals. To ensure alignment, review the code against READMEs, design documents, and Architecture Decision Records (ADRs) to confirm it addresses the right problem [1][10].
Ask the AI about its assumptions and how it handles edge cases. This can uncover hidden logic that may not align with your needs. Be cautious of non-existent APIs - sometimes the AI fabricates function calls or libraries that sound plausible but don’t actually exist [1][2].
Pay special attention to edge cases. AI models often miss boundary conditions like null values, empty arrays, negative numbers, or unexpected inputs [2][10]. For example, in October 2025, OpenAI integrated an automated code reviewer into GitHub workflows, processing over 100,000 pull requests daily. The system revealed that 52.7% of reviewer comments led to code changes, proving that even automated reviews can catch critical issues [7].
Once you’ve ensured the code meets requirements, move on to integration and error handling checks.
Test Integration and Error Handling
Evaluate how the AI-generated code interacts with your existing systems. Look for performance bottlenecks, such as sequential I/O calls within loops. AI often generates code that performs hundreds of serial network requests instead of parallelizing them, potentially leading to system outages [10]. As SonarSource highlights:
"Accountability here means catching this subtle but critical flaw" [10].
Ensure the code adheres to your project’s error-handling conventions. For instance, if your codebase uses custom ApiError classes, verify that the AI didn’t default to generic exceptions [10]. Providing the AI with context - like architectural diagrams, design documents, or existing error-handling files - can help it generate more accurate code. Be specific in your prompts; for example, instead of a generic request, specify, “I’m using the Zod validation library” to guide the AI [10].
Also, review concurrency to prevent issues like deadlocks and race conditions [11]. To make the AI’s reasoning more effective, keep functions concise - under 50-100 lines, maintain a cognitive complexity below 15, and limit nesting depth to four levels or fewer [10].
Run Automated Tests
Before diving into a manual review, run automated tests and static analysis tools. These can catch basic errors like compilation issues, warnings, or syntax problems, saving valuable reviewer time [1][8]. If your test coverage is lacking, use AI tools to generate unit tests for the newly added code [9].
Adopt quality standards like the "Sonar way for AI Code", which requires at least 80% test coverage for new code and limits duplication to 3% or less [12].
Use tools that analyze your entire repository, not just isolated code snippets. Context-aware systems powered by Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) can identify problems where AI-generated changes conflict with dependencies [7][3]. By late 2025, 46% of AI-generated comments on AI-produced code led to functional changes, showcasing the value of automated review systems [7].
| Verification Step | Tool/Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Check | Automated Tests / CI | Ensure code compiles and passes existing logic |
| Context Alignment | AI Prompts / README | Verify code matches business intent and design |
| Edge Case Review | Manual / AI Analysis | Identify missing error handling or boundary gaps |
| Dependency Audit | Dependabot / CodeQL | Check for insecure or non-existent packages |
| Integration Test | Repo-wide AI Review | Confirm interactions with existing system components |
Security and Vulnerability Checklist
AI-generated code tends to introduce more vulnerabilities compared to code written by humans. Studies reveal that pull requests created by AI contain 1.57 times more security issues, with AI-generated code being 2.74 times more likely to introduce Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities and 1.91 times more likely to include insecure object references. These aren't just theoretical risks - they're well-documented patterns that demand thorough code reviews [5].
Check Input Validation
Always treat input handlers as potential weak points. AI tools often overlook proper sanitization, leaving the door open for SQL injection and XSS attacks. Ensure that database operations use parameterized queries instead of string concatenation. Additionally, all user inputs should pass through validation layers before being processed [16].
A cautionary tale: In March 2025, Leonel Acevedo, founder of Enrichlead, faced a devastating breach when attackers bypassed the paywall due to missing authentication logic in AI-generated code. They exploited the lack of input validation and rate limiting, maxing out API keys and forcing the startup to shut down permanently [15]. This real-world example highlights why input handling from AI tools should never be trusted without verification.
Be on the lookout for risky functions like eval(), which should be replaced with safer alternatives like JSON.parse() [17]. Also, ensure that all form submissions, API endpoints, and file uploads are sanitized according to OWASP standards [16].
After addressing input validation, shift focus to external dependencies.
Review Dependencies and Licenses
AI tools frequently suggest outdated or insecure libraries, and in some cases, even recommend non-existent packages. For example, in August 2025, an AI-generated pull request for the NX build tool introduced a command injection vulnerability. The issue arose from using pull request titles directly in shell commands without proper sanitization. This oversight allowed an attacker to steal NPM publishing tokens, leading to a compromised update that affected over 1,400 developers [15].
When reviewing dependencies, verify that every suggested library exists, is actively maintained, and has no known vulnerabilities. Look for hardcoded secrets like API keys or database credentials, which AI tools often include despite security best practices [6][14]. Replace these with environment variables or secure secret managers like AWS Secrets Manager or Vault.
Be aware of "slopsquatting", where malicious packages are designed to resemble legitimate libraries, targeting AI-generated suggestions [1][14]. Vigilance here can prevent significant security incidents.
Finally, bolster your defenses with automated scanning tools.
Apply Security Scanning Tools
Automated security tools are essential for catching vulnerabilities that AI-generated code may introduce. Tools like SonarQube, Semgrep, and CodeQL can identify risky patterns, such as improper password handling (which happens 1.88 times more often in AI-generated code) and insecure deserialization (1.82 times more likely) [5].
Set up quality gates tailored for AI-generated code. For instance, SonarQube's "AI Code Assurance" requires an 'A' security rating and at least 80% test coverage before code can be merged [12][20]. Use Codacy Guardrails directly within your IDE to scan and fix security flaws before committing, and enable Semgrep's Shadow AI Scan to identify unauthorized use of LLM libraries that might expose sensitive data [18][19].
These tools work alongside functional and quality checks to create a thorough review process.
| Tool | Security Function | AI-Specific Feature |
|---|---|---|
| SonarQube | SAST / Quality Gates | AI Code Assurance Badge with 'A' rating requirement [12] |
| Semgrep | SAST / Secret Scanning | Shadow AI detection for unauthorized LLM usage [19] |
| Codacy | SCA / SAST / DAST | Real-time IDE scanning across 40+ languages [18] |
| CodeQL | Semantic Analysis | GitHub integration for vulnerability detection [17] |
| Dependabot | Dependency Alerts | Automated updates for insecure packages [1] |
David Loker, Director of AI at CodeRabbit, puts it succinctly:
"AI coding tools dramatically increase output, but they also introduce predictable, measurable weaknesses that organizations must actively mitigate" [5].
Code Quality and Maintainability Checklist
When working with AI-generated code, maintaining high code quality is essential to avoid long-term technical debt. While such code might function correctly, it often hides structural flaws that make it harder to maintain. AI-generated code can be verbose, repetitive, and less organized compared to code written by humans.
Check Readability and Style
Start by ensuring that variable, function, and class names are descriptive and follow the conventions of the programming language you're using - like PascalCase for Java or snake_case for Python [21]. AI tools often produce generic names like data or processor, which fail to describe their purpose clearly. Make sure the code aligns with your project's style guide to maintain consistency across the codebase [21].
Look out for violations of the DRY (Don't Repeat Yourself) principle. AI often duplicates code blocks instead of creating reusable functions [21][2]. As Sara Verdi, a Software Engineer at Graphite, puts it:
"Treat AI-generated code as a draft... Humans excel at contextual judgment and nuanced decisions, while AI can handle the busywork" [2].
If refactoring AI-generated code seems more time-consuming than rewriting it, it’s better to start fresh [1].
Before diving into a manual review, run automated formatters like Prettier or Black to handle basic style issues [3]. Use linters like ESLint to catch common mistakes automatically. For example, in a study of AI-generated pull requests at OpenAI, developers made changes based on AI review comments in 46% of cases, with over 80% of developer feedback on those comments being positive [7].
Once you've reviewed the code's style, shift your attention to comments and documentation to ensure they provide meaningful context.
Verify Comments and Documentation
AI-generated comments often describe what the code does rather than why it exists, which can lead to unnecessary clutter [21][10]. Additionally, comments might not reflect the final logic if the code has been modified after generation. Focus on ensuring comments explain complex business rules, edge cases, or architectural decisions that aren’t immediately clear from the code itself.
Check that all public functions and classes include clear and concise docstrings. These should help future developers understand the purpose and origin of the code without needing to dig through the implementation.
Measure Performance and Resource Use
Good code quality also involves ensuring the code performs efficiently and manages resources effectively. AI models can struggle with performance optimization, sometimes introducing bottlenecks. For example, avoid sequential I/O operations inside loops (e.g., using forEach instead of Promise.all), as they can significantly slow down execution [10].
Keep functions concise - ideally under 100 lines - with no more than four levels of nesting and a cognitive complexity score below 15 [10]. As SonarSource highlights:
"Accountability... is no longer just about owning what you type; it's about being a deeply skeptical senior reviewer for every line of code you accept" [10].
Ensure proper resource management by checking for missing deallocation of memory or file handles. Use language-specific constructs like try-with-resources to prevent resource leaks [21]. Eliminate redundant variables and logic that add unnecessary complexity without improving functionality [10][2].
AI-Specific Code Review Checklist
AI-generated code often brings unique challenges, producing more issues compared to human-written code [4][5]. These challenges typically arise from the way AI systems interpret requirements and create solutions. The following sections outline key areas to focus on when reviewing AI-generated code.
Identify Incorrect Assumptions
AI systems frequently generate code that appears correct but contains serious logical flaws. A common issue is hallucinated APIs, where the AI fabricates libraries, packages, or API endpoints that don’t actually exist [1]. It’s essential to manually verify every AI-suggested dependency to ensure it exists and is actively maintained. Also, be alert for "typosquatting" attacks, where malicious actors create fake packages with names similar to those commonly hallucinated by AI models [1].
Another prevalent problem is the tendency of AI to assume "happy path" scenarios, ignoring critical edge cases like null values, invalid inputs, or boundary conditions. This can lead to logic errors [5]. As David Loker, Director of AI at CodeRabbit, explains:
"AI coding tools dramatically increase output, but they also introduce predictable, measurable weaknesses that organizations must actively mitigate" [5].
Avoid relying on AI-generated suggestions that bypass failing tests. Instead, prompt the AI with questions like, "What edge cases or business logic might this code overlook?" [1].
Verify License Compliance
AI models can sometimes replicate open-source code blocks verbatim, potentially leading to intellectual property issues. To mitigate this, use Software Composition Analysis (SCA) tools like SonarQube, Semgrep, or Dependabot to scan for reused code fragments that could include protected intellectual property.
Additionally, ensure that AI-suggested dependencies align with your project's licensing requirements. For instance, adding AGPL-3.0 code to an MIT-licensed project could create compatibility issues [1]. You can ask the AI to audit its own suggestions with prompts like, "Analyze the attached package.json file and list all dependencies along with their licenses." Tagging AI-generated code in Git commits can also help in future legal or security reviews.
Compare Against Project Standards
Beyond basic checks, ensure that AI-generated code aligns with your project’s established guidelines. Tools like CodeRabbit or Graphite Agent can be configured with custom YAML rules to enforce project-specific patterns [23][13]. Providing the AI with relevant context - such as your project's README, documentation, and CONTRIBUTING.md files - can help ensure it adheres to your conventions [1]. Automated linters can further catch naming and style inconsistencies, which AI often introduces [4].
A multi-layered review process works best: start with automated linting and static analysis, follow with an AI review, and conclude with human validation [24][3]. As Jamie Schiesel, Fractional CTO at MetaCTO, emphasizes:
"The human developer provides the strategic intent; the AI provides a tactical implementation" [24].
Tools and Automation for Code Reviews
Expanding on the idea of review checklists, automating AI-driven code reviews can help catch predictable errors on a large scale. This approach reduces review time by 28% [27].
Let’s explore some specific AI tools that can simplify the code review process.
Use AI-Assisted Review Tools
Clacky AI functions as a cloud-based coding studio with built-in review capabilities. Its Task Time Machine feature logs every AI action, making it easy to review or undo changes. Pricing starts at $29 per seat per month, which includes 2,000 monthly credits and support for 15–20 tasks.
CodeRabbit integrates more than 40 linters and security scanners directly into pull requests. It offers concise, AI-generated summaries and enables one-click fixes for identified issues.
Graphite Agent uses a RAG model to deliver feedback tailored to your codebase. It scans pull requests for repetitive patterns and common security flaws, providing actionable suggestions and one-click fixes.
OpenAI’s internal deployment of GPT-5.1-Codex showcases the impact of automation. This tool processes over 100,000 external pull requests daily, with a 52.7% action rate. However, the OpenAI Codex team stresses the importance of oversight:
"We cannot assume that code-generating systems are trustworthy or correct; we must check their work." [7]
Manage Dependencies and Vulnerabilities
Automated tools play a critical role in verifying dependencies and identifying vulnerabilities. For example, Dependabot monitors outdated libraries and flags security risks, while tools like CodeQL and Semgrep detect fabricated APIs.
To block pull requests with high-severity CVEs or hardcoded secrets, you can establish automated policies [28]. Integrating tools like Snyk into CI/CD pipelines via webhooks triggers scans as soon as a pull request is opened. This approach enhances security by embedding vulnerability checks into your development workflow. Given that 67% of developers report spending additional time debugging security issues in AI-generated code [26], such automation can significantly ease the debugging workload.
Compare Manual vs. Automated Review Time
| Review Method | Time Investment | Error Detection Type | Context Awareness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Review | High (Hours/Days) | Complex logic, architecture, intent | High (Human domain knowledge) |
| Static Analysis | Low (Seconds) | Syntax, style, known vulnerabilities | Low (Pattern matching) |
| AI-Assisted Review | Medium (Minutes) | Edge cases, logic bugs, documentation | High (Repo-wide RAG models) |
Combining automated testing, AI-assisted reviews, and human validation creates a robust workflow, especially for high-risk code [3]. This layered approach not only ensures thorough code quality checks but also speeds up feature release cycles by 30% [25].
Deployment Readiness Checklist
After ensuring your code meets quality and security standards, it's crucial to apply the same level of diligence to your deployment process. AI-generated code must be prepared to handle real-world traffic without disrupting existing systems. Here's why it matters: fixing issues during the review phase is 10–100 times cheaper than addressing them after deployment [29]. Below are key steps to ensure a smooth and reliable deployment.
Validate CI/CD Pipeline
Your CI/CD pipeline should act as a gatekeeper, blocking merges unless all status checks are green. Use policy-as-code to automatically fail pull requests that include high-severity CVEs or hardcoded secrets [28]. For compliance with frameworks like SOC 2, generate a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) for every build [28]. Tools like CodeQL, SonarQube, and Semgrep can help identify errors and confirm that dependencies aren't fabricated [1].
To simplify audits, tag commits to distinguish between AI-generated and human-written code [28]. Keep automated test runs efficient - under 10 minutes - and aim for at least 60% test coverage as a baseline [29].
Once the pipeline is validated, focus on safeguarding your APIs.
Check API Usage and Rate Limits
Separate staging and production environments to prevent testing from interfering with live operations. Set custom rate limits to protect your systems [30]. Use dashboards to monitor API key usage and set alerts for when spending approaches predefined limits [30]. Canary deployments are a must - they help catch latency spikes or error rate increases before they affect all users [31].
For added control, assign distinct API keys to each environment, pin model versions to prevent unexpected changes, and use automated rollback triggers if performance metrics dip [30] [31].
Run Final Pre-Deployment Tests
Before going live, mirror production requests in a read-only mode for shadow testing. This allows you to compare outputs and performance without impacting users [31]. Golden Master tests with production-like data can help identify any semantic inconsistencies. Stress tests under various conditions - normal, peak, and adverse - are essential to confirm that your system can auto-scale and remain resilient.
For example, in October 2025, OpenAI introduced an agentic code reviewer (powered by gpt-5-codex) into its engineering workflow. This tool reviewed over 100,000 external pull requests daily, with a 52.7% success rate in prompting authors to address review comments through code changes [7].
Finally, ensure your metrics, traces, and logs align with established baselines. Conduct monthly rollback drills to guarantee you can quickly revert AI-generated artifacts if needed [31].
Conclusion: Key Points for Reviewing AI-Generated Code
When working with AI-generated code, thorough reviews are essential to deliver reliable software and prevent technical debt from piling up. Your review process should focus on functional correctness, security, code quality, and AI-specific risks like hallucinated APIs. Addressing these areas helps uncover hidden errors and mitigate potential security vulnerabilities.
The importance of such reviews is underscored by research showing that 19.7% of packages suggested by AI coding assistants didn’t actually exist. This highlights the serious risk of dependency hallucinations [22]. Taking these precautions ensures your code is solid, secure, and ready for deployment.
FAQs
What are the top security risks in AI-generated code?
AI-generated code can sometimes come with security risks that developers must tackle head-on. Here are a few common vulnerabilities to watch out for:
- Injection attacks: These include SQL or command injection, where unsafe inputs can compromise your application.
- Insecure defaults or flawed logic: These can lead to unexpected or unsafe behaviors in the code.
- Malicious code: This might sneak in through training data or outdated libraries.
- Prompt injection vulnerabilities: These can expose sensitive information or confidential data.
- Unpatched open-source components: These may harbor exploitable weaknesses if not updated.
To address these challenges, always thoroughly review AI-generated code, stick to secure coding practices, and ensure all dependencies are up to date. Tools like automated scanners and security-focused software can make identifying and fixing vulnerabilities much easier.
How do I ensure AI-generated code meets my project’s standards?
To make sure AI-generated code meets your project’s standards, start by setting clear expectations. Define the inputs and outputs, performance goals, and security requirements upfront. Use these criteria to build a checklist that covers key aspects like functionality, readability, security, and performance. Encourage developers to go through this checklist as part of a self-review before the code goes to peer review.
When it’s time for the review, combine human expertise with automated tools. Run unit and integration tests, check for any compilation errors, and use static analysis tools to spot vulnerabilities or dependency issues. If your project demands high performance, benchmark the code to see if it aligns with your goals. Don’t forget to ensure the code follows your team’s style guide and adheres to architectural standards. By sticking to a structured review process, you can make AI-generated code dependable and ready for production.
What are the best tools for reviewing AI-generated code automatically?
Several tools are available to simplify the review process for AI-generated code, helping to catch bugs, security vulnerabilities, and performance issues before deployment. Tools like GitHub Copilot and Copilot Chat can suggest fixes during development, making coding more efficient. Meanwhile, CodeQL excels at static analysis, and Dependabot keeps your dependencies updated. These tools can easily integrate into continuous integration (CI) workflows.
For maintaining code quality and security directly within your IDE, SonarQube and SonarLint from SonarSource are excellent choices. On the other hand, Codacy provides an AI Reviewer capable of performing linting, security checks, and test coverage analysis for repositories on platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket.
Emerging tools such as Qodo, Sweep AI, and Tabnine take things further, offering comprehensive pull request reviews, vulnerability scans, and even auto-fixes. If you're looking for a more advanced solution, OpenAI’s Codex CLI can analyze entire repositories to uncover critical bugs and alignment issues. By using these tools, you can streamline the code review process and ensure that AI-generated code is ready for production.









