What is Automated Code Generation?
Automated code generation uses AI, specifically large language models (LLMs), to turn plain-English prompts into functional code. Unlike low-code platforms, these tools create custom code tailored to your input. They help developers save time, reduce repetitive tasks, and improve productivity. For example:
- 88% of developers report feeling more productive with tools like GitHub Copilot.
- 96% complete repetitive tasks faster using AI assistance.
These tools work by predicting code based on context, learning from massive datasets of programming languages. They integrate with IDEs like VS Code, support over 20 programming languages, and assist throughout the development process - from writing code to debugging and testing.
While AI speeds up development, human oversight is critical. AI-generated code can sometimes include errors, vulnerabilities, or licensing issues. Developers must review, test, and secure the code to ensure reliability.
Popular tools include GitHub Copilot, Replit AI, and Cursor. Each offers unique features like real-time suggestions, browser-based coding, and multi-file refactoring. For example, Replit AI allows users to create deployable apps directly from prompts, while ClackyAI automates GitHub issue-to-PR workflows.
AI tools are transforming software development, letting developers focus on creative and strategic tasks while automating the tedious parts. But they’re not perfect - human expertise is still essential for quality and security.
Coding with AI #1 - Tools, Models & Copilot Setup
How Automated Code Generation Works
Automated code generation hinges on Large Language Models (LLMs), which are trained on vast datasets of public source code from platforms like GitHub, alongside natural language text[1]. These models learn programming syntax, patterns, and paradigms by analyzing billions of lines of code. Using this knowledge, they predict the next logical code segment based on the current context[1]. Let’s dive into how machine learning and natural language processing come together to power these tools.
Machine Learning-Driven Code Generation
Using trained LLMs, these tools predict code sequences, simplifying the development process. They analyze patterns in your code and suggest the next logical steps based on the surrounding context. With attention mechanisms, they focus on the most relevant parts of the code to ensure better accuracy.
In February 2025, the AWS Q Developer team reported a 39% improvement in code generation success rates on the MBPP benchmark. They achieved this through supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning, leveraging models like StarCoder-15B and CodeLlama-13B[8]. Their process included generating synthetic debugging data, enabling models to not only identify but also fix functional errors in their outputs.
Advanced models, such as Code Llama with its 70 billion parameters, excel at handling complex programming scenarios[7]. Similarly, GPT-4.1 supports massive context windows of up to 1 million tokens, enabling it to analyze entire large-scale codebases in one go[6].
Natural Language to Code Conversion
These tools can interpret plain English comments like // create a function that validates email addresses and turn them into working code. This goes beyond simple autocomplete; tools like GitHub Copilot Chat and Qodo provide conversational interfaces, allowing users to refine their code through dialogue[9]. You can ask the AI to explain logic, debug errors, or even refactor entire sections - all in plain English.
However, these tools aren’t foolproof. They can sometimes generate "hallucinations", where the code appears syntactically correct but is logically flawed or references non-existent functions. As Albert Ziegler, Principal Researcher at GitHub, explains:
"Computer generated code is good enough that it doesn't leave any particular traces and normally has no clear tells"[1]
This highlights the importance of thoroughly reviewing AI-generated code.
Integration with Development Workflows
AI coding tools are designed to integrate seamlessly into existing development workflows. They can be added as extensions to popular IDEs like VS Code and JetBrains, offering real-time suggestions while you type[2]. These tools support over 20 programming languages, including Python, JavaScript, Java, C++, Go, and TypeScript[2].
Beyond the editor, AI tools are embedded throughout the development lifecycle. They can generate pull request descriptions, review code changes, and even create new pull requests to address bugs[10]. They also integrate with project management and communication tools, streamlining code review and deployment processes[11]. Some tools go a step further by auto-generating unit tests, identifying security vulnerabilities, and suggesting fixes for broken tests in real time[1].
For example, GitHub’s "Copilot Spaces" allows developers to share the context of a coding task with their teammates, fostering better collaboration[10]. Despite these advancements, human oversight remains critical. Always pair AI-generated code with standard code reviews and automated vulnerability scanners to ensure security and reliability[5].
Benefits and Challenges of Automated Code Generation
This section dives into the upsides and hurdles of AI-driven code generation. While it can significantly boost productivity, it also introduces risks that require careful management.
Main Benefits
AI coding tools are excellent at handling repetitive tasks, freeing developers to focus on more complex challenges. In fact, 96% of developers report completing repetitive work faster, and 74% say they can dedicate more time to engaging and creative tasks[4].
The productivity perks don’t stop at individual developers. These tools offer real-time suggestions for best practices, flag security vulnerabilities as you code, and recommend refactoring to enhance long-term maintainability[12][3]. They also help streamline workflows by minimizing context switching - allowing developers to access documentation, search code snippets, and even run tests, all within their IDE using natural language commands[12].
For teams, AI lowers the learning curve. Junior developers get tailored guidance and code explanations, while Product Managers can create functional prototypes from simple prompts or screenshots - no manual coding required[12][14]. This accessibility speeds up the entire product development process, from brainstorming to final handoff. However, these advantages come with challenges that demand attention.
Common Challenges
AI-generated code isn’t perfect and requires constant oversight. A 2023 study found that ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot produced correct code 65.2% and 46.3% of the time, respectively. When suggestions were accepted without review, developer productivity actually dropped by 19%[19][13].
Security is another major concern. AI models trained on public datasets can unintentionally reproduce flawed code patterns, leading to risks like SQL injection, weak authentication, or poor input validation[15][16]. This can be deceptive because the code often looks polished but hides critical vulnerabilities. As Fergal Glynn from Mindgard aptly notes:
"AI-generated code may look clean and functional, but beneath the surface, it can harbor critical vulnerabilities."[15]
There’s also the issue of skill erosion. Relying too heavily on AI can weaken developers’ core coding abilities and reduce their understanding of system architecture, making debugging and long-term maintenance much harder[15][18]. Legal risks further complicate things, as AI models might reproduce copyrighted code or violate licensing agreements, leading to potential intellectual property disputes[15][17][18].
Benefits vs. Challenges Comparison
| Benefit | Associated Challenge | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Speed | Vulnerable or insecure code | Use automated security tools and manual reviews |
| Reduced Manual Effort | Rising technical debt | Regular refactoring and metadata-driven design |
| Faster Prototyping | Missing business logic context | Human oversight for critical rules |
| Consistent Code Patterns | Developer skill atrophy | Continuous training and hands-on coding labs |
| Scalability | IP and licensing risks | Implement SBOM and license-checking tools |
AI-generated code should always be treated as a starting point, subject to thorough testing and review[15][4]. By 2025, over 82% of developers will use AI coding tools weekly, and 59% will rely on three or more tools regularly[13]. Striking the right balance between benefits and challenges is key to successfully integrating these tools into your workflows.
sbb-itb-c336128
Tools for Automated Code Generation
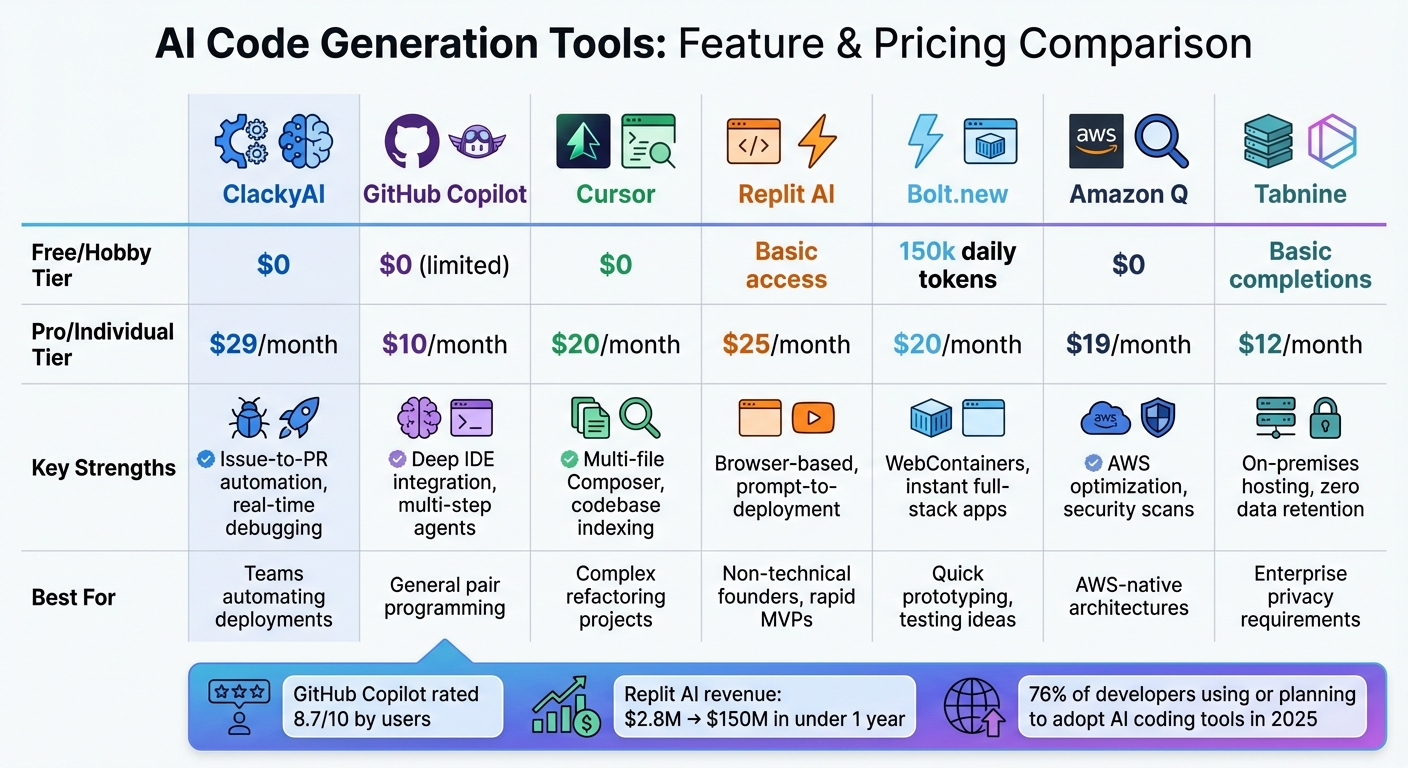
AI Code Generation Tools Comparison: Features, Pricing, and Best Use Cases
The demand for AI-powered code generation tools is on the rise, with over 76% of developers already using or planning to adopt these solutions this year [20]. The industry is evolving quickly, moving from basic autocomplete tools to more advanced "agentic" systems capable of planning, executing, and deploying code changes autonomously [20][23]. These tools come in a variety of offerings, from free versions to enterprise-level solutions.
Tool Options
GitHub Copilot is a popular choice for developers, offering inline code suggestions, natural language chat, and autonomous agents to handle multi-step workflows. It integrates effortlessly with VS Code and JetBrains IDEs, making it a convenient option for those who prefer to stick with their current tools. Reviews have given it an 8.7/10 composite score, with users highlighting its impressive "next edit" prediction capabilities [24].
Cursor is a version of VS Code designed for AI-driven interactions. Its standout feature, "Composer", handles tasks like multi-file code generation and deep indexing of codebases, making it a strong choice for complex refactoring projects [22][23].
Replit AI focuses on simplicity and speed, enabling developers to go from a natural language prompt to a deployed application without any local setup. This browser-based IDE launched Agent 3 in September 2025, showcasing its ability to autonomously handle tasks for up to 200 minutes at a time [25]. Replit's growth has been remarkable, with annualized revenue jumping from $2.8 million to $150 million in under a year [25].
"We were the first to make vibe-coding a reality for individuals with no prior coding experience across the world."
– Amjad Masad, CEO, Replit [25]
Bolt.new is an innovative tool that uses WebContainers to instantly generate full-stack applications. Whether you're working with React or Next.js, Bolt.new allows you to scaffold, run, and deploy directly in your browser [21][22].
ClackyAI specializes in automating workflows, particularly in transforming GitHub issues into production-ready pull requests. This end-to-end automation makes it a practical choice for teams looking to streamline their deployment processes.
Below is a comparison of these tools, highlighting their features and pricing.
Feature and Pricing Comparison
| Tool | Free/Hobby Tier | Pro/Individual Tier | Key Strengths | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClackyAI | $0 | $29/month | Issue-to-PR automation, real-time debugging | Teams automating deployments |
| GitHub Copilot | $0 (limited) | $10/month | Deep IDE integration, multi-step agents | General pair programming |
| Cursor | $0 | $20/month | Multi-file Composer, codebase indexing | Complex refactoring projects |
| Replit AI | Basic access | $25/month | Browser-based, prompt-to-deployment | Non-technical founders, rapid MVPs |
| Bolt.new | 150k daily tokens | $20/month | WebContainers, instant full-stack apps | Quick prototyping, testing ideas |
| Amazon Q | $0 | $19/month | AWS optimization, security scans | AWS-native architectures |
| Tabnine | Basic completions | $12/month | On-premises hosting, zero data retention | Enterprise privacy requirements |
For individual developers, GitHub Copilot stands out as one of the most affordable options at $10/month. For small teams and startups, Cursor and GitHub Copilot often provide the best balance between functionality and cost [26][27].
These tools not only simplify coding but also integrate smoothly with modern deployment pipelines, making it easier to ship products faster and more efficiently.
Case Study: ClackyAI
ClackyAI is a prime example of a tool designed for deployment-first automation. It manages the entire workflow, from monitoring GitHub issues to generating production-ready pull requests. By analyzing code changes and generating modifications autonomously, it helps teams save time and reduce manual effort.
One of its standout features is real-time debugging, which monitors logs and suggests fixes proactively. This significantly reduces the time it takes to identify and resolve issues.
For teams exploring deployment automation, ClackyAI’s free Hobby plan includes 300 monthly credits and 2c/4G computing resources, which can handle 1–3 tasks per month. The Pro plan, priced at $29/month, scales up to 2,000 base credits and 1,000 bonus credits monthly. This tier supports 15–20 tasks and includes up to 10 workspace seats with real-time collaboration. Additionally, its "Task Time Machine" feature provides a detailed audit trail of all AI modifications, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of unreviewed code changes.
Adding Automated Code Generation to Deployment Pipelines
Workflow Integration Methods
Bringing AI-driven code generation into your deployment pipeline involves strategically embedding it at key stages. For instance, you can integrate AI agents directly into GitHub using specialized apps that handle repository management, branch creation, code commits, and pull request reviews [11]. This approach ensures a smoother and safer deployment process.
To prepare for production, it's crucial to use sandboxed environments. These isolated setups allow AI agents to install dependencies, test changes, and perform automated vulnerability scans before any code is merged into the main branch [1][11].
"The answer is not if you have GitHub Copilot, use a vulnerability checker. The answer is always use a vulnerability checker." – Albert Ziegler, Principal Researcher, GitHub [1]
For testing, tools like Playwright can record user interactions and convert them into test scripts, which can then be integrated into your pipeline [28][4]. If you need more advanced customization, Python SDKs offer programmatic control over AI agents, letting you design workflows tailored to your team's specific needs [11].
Despite these advancements, human oversight remains indispensable. Developers play a critical role in reviewing AI-generated code to ensure it aligns with the team’s architecture and quality standards. This combination of automation and human expertise creates a balanced and reliable pipeline for deployment.
Practical Use Cases
Real-world examples highlight how AI can speed up the path from concept to production. In March 2025, developer Colin Matthews demonstrated this by prototyping an "Apollo scheduler" in just 10 minutes using Bolt [14]. He went further, creating a full-stack referral app with Stripe integration, leveraging Replit's built-in database and authentication services. The result? A fully functional prototype deployed in minutes - without relying on external cloud infrastructure [14].
Small teams and indie developers are also embracing multi-tool workflows. Matthews documented a process using Lovable for design, syncing code to GitHub, and debugging with Cursor [14]. This pipeline, which starts with cloud-based development environments and transitions to AI-enhanced IDEs, shows how flexible AI-assisted automation can be for teams of all sizes and stages.
Product managers are getting in on the action as well. Instead of static sketches in Product Requirement Documents, they now use AI tools to create interactive prototypes. These prototypes allow developers to test and refine ideas immediately, cutting down on iteration time [14].
For teams focused on deployment-first strategies, tools like ClackyAI offer a streamlined solution. ClackyAI monitors GitHub issues, generates production-ready pull requests, and provides real-time debugging. With a Pro plan priced at $29 per seat per month - covering 15–20 tasks monthly and supporting up to 10 seats - it’s a practical choice for small teams looking to enhance their deployment workflows efficiently.
Conclusion
Automated code generation is changing the game for software development. With 88% of developers reporting increased productivity thanks to AI-powered coding assistants [1], and 96% completing repetitive tasks faster [4], these tools are proving their worth. But let's be clear - this isn't about replacing human expertise. It's about cutting out the tedious tasks that slow developers down.
The shift in how developers work is undeniable. Instead of writing every single line of syntax, they're focusing on bigger-picture priorities like system architecture, security, and solving strategic challenges. As Albert Ziegler from GitHub aptly puts it:
"Refusing adoption would be like asking an office worker to use a typewriter instead of a computer" [1]
The tools are already available, the workflows are tested, and the productivity boosts are measurable.
Here's a practical takeaway: identify one repetitive task in your workflow - maybe it's generating boilerplate code, writing unit tests, or scaffolding API endpoints - and try integrating an AI assistant into that process. Use human-in-the-loop reviews to ensure quality, pair AI outputs with vulnerability checkers, and treat the generated code as a starting point that still needs your expertise. Whether you're exploring tools like Cursor for IDE integration or ClackyAI for deployment-focused workflows, the key is to test, refine, and find what works best for your team.
As highlighted throughout this article, the role of the developer isn't disappearing - it's evolving. You're becoming the architect, the reviewer, and the guardian of quality. While AI handles repetitive patterns, you focus on the decisions that truly matter. This is the future of software development, and it's already here.
FAQs
How do AI tools help ensure the security of the code they generate?
AI-powered code generation tools are designed with security in mind, embedding protective measures right into their processes. These tools are typically trained on extensive, well-reviewed codebases and follow established security practices. This includes steering clear of risky functions, employing parameterized queries, and adhering to organizational security guidelines. Many tools also offer real-time feedback, flagging potentially unsafe code and recommending safer alternatives.
To bolster security further, these tools often rely on automated static analysis and AI-driven vulnerability scanning. For instance, some platforms incorporate AI-based scanners into code review workflows, identifying issues like dependency vulnerabilities or insecure coding patterns before the code goes live. In many cases, CI/CD systems make security a mandatory checkpoint, ensuring that unsafe code is blocked from reaching production.
By integrating secure training methods, instant feedback, and automated security checks, these AI tools empower developers to create reliable, production-ready code while reducing the risk of vulnerabilities.
What are the challenges of using automated code generation tools?
Automated code generation tools can be incredibly helpful for handling repetitive tasks, but they aren't without their challenges. One major issue is their difficulty in tackling complex problems that demand deep domain knowledge or creative thinking - areas where human expertise still excels.
Another concern is the potential for security risks. For example, auto-generated code might unintentionally introduce vulnerabilities, like SQL injection flaws or performance bottlenecks, making thorough developer reviews essential. There's also the risk of licensing or intellectual property conflicts, as some generated code may inadvertently replicate open-source material without proper acknowledgment.
On top of that, maintaining AI-generated code can be tricky. It often suffers from low readability, excessive abstraction, or unnecessary complexity, all of which can add to technical debt. To ensure the software is of high quality and reliable, human oversight, along with regular refactoring, remains indispensable.
How can developers use AI tools without losing their coding skills?
To get the most out of AI tools while keeping your coding skills sharp, it's important to think of AI as a partner rather than a replacement. These tools can handle repetitive tasks, offer suggestions for improvement, and highlight best practices. However, it's essential to review and understand these recommendations to stay actively involved in the coding process. This way, you can make thoughtful decisions about the structure and functionality of your code.
To maintain your skills, set aside time for manual coding. Work on small projects or solve algorithmic challenges without relying on AI. This practice strengthens your problem-solving abilities and makes it easier to debug or refine AI-generated code when necessary. By balancing the efficiency of AI tools with regular hands-on coding, you can enhance productivity while continuing to build your expertise.









